How electronic is damaged?
Atmospheric discharge is not only the flow of electric current of enormous values, it is also a series of spark overs between metal structures and conductors as a result of a strong electric field. It is also an electromagnetic pulse that penetrates all non-shielding materials.
Each of the above factors will affect the device and may cause damage to it:
1. Increase in supply voltage or signal voltage
It occurs when a spark over to one of the conductors causes an increase in the potential between the conductors. Increased voltage causes more current to flow through the electronic components, increasing the power lost to them. Depending on the ability to convert power into heat, the time of the increased current flow and the applied ESD protections, electronic components are damaged or not.
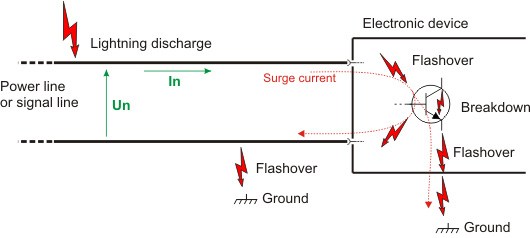
In the diagram above, there is a spark over to one of the power wires or the signal line. This causes the nominal voltage (Un) and the rated current (In) to be exceeded many times, and the accumulation of power in components, power which cannot be discharged to the environment - as a result, the electronic components are overheated. High voltage causes a breakdown inside the components, causing them to short-circuit and, depending on the current, the circuit boards will burn through. The potential of a spark-over looking for an way to the ground causes further spark-overs between many components and even individual devices, creating further destruction.
2. Increase in the current flow of signal interfaces
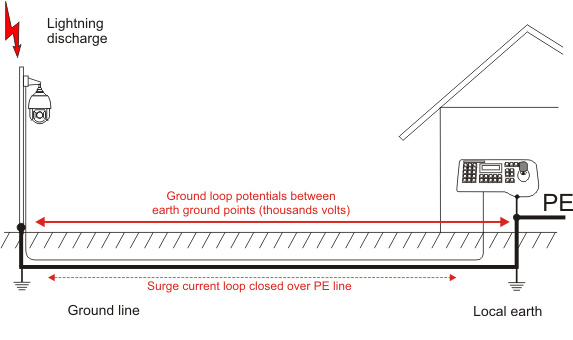
During the discharge, in the ground and on its surface, a large surge current flows towards the place of lightning strike, which is the result of the neutralization of the charge between the clouds and the ground. This effect is known as step voltage or as the instantaneous potential difference between the grounded points of the installation. Depending on the location of the devices, the distance between the components of the electronic system, power sources and local grounding, an equalizing current pulse is generated between them. Due to the greater earth resistance, the current pulse is compensated by the wires and the communication interfaces connected with it, causing them to overcurrent and damage them.
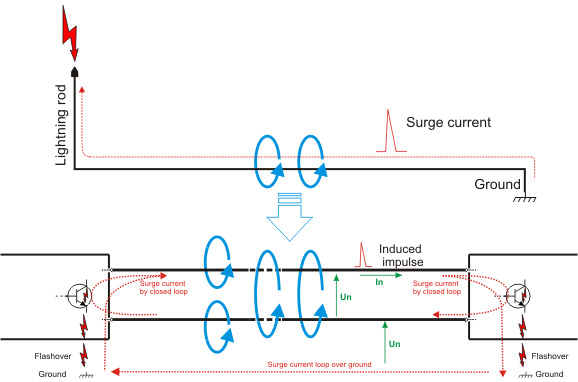
3. The induction of an electromagnetic pulse in the wires
When lightning strikes grounded cables or metal structures, a very strong magnetic pulse is generated. Penetrating into other cables, this impulse induces an electric impulse, the energy of which depends on the distance from the discharge location, the type of cable and the way it is arranged. The voltage impulse poses an identical threat to the electronics as described in point 1 - it creates a temporary increase in voltage on the power and signal lines. As a result of discharges in clouds, the balance of electric charges in overhead lines is also disturbed, causing sudden flows of electric current between the power source and receivers.
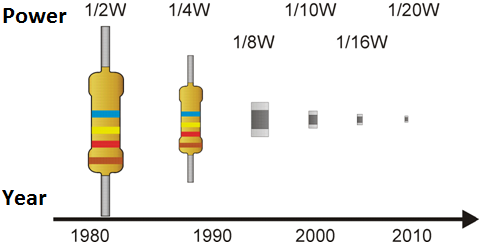
Electronics over the past 30 years has undergone enormous progress in miniaturization. This brings many benefits, including:
- Increased computing power
- Reducing the dimensions, allowing mobility
- Reduced energy consumption and lower energy losses
- Less consumption of precious materials
- Lower prices of electronic devices
The reduction of components resulted in a significant reduction in supply voltages and communication interfaces of systems with a high scale of integration (computing processors, DSP, PLD, memory). Processors in the 90s of the last century were usually powered by 5V and a temporary excess of 1V was tolerated by them. Currently, high-scale integration systems supply voltage even below 1V and its increase by 1V causes very quick damage.
Another aspect is the very small dimensions and high density of components on the electronics board, which mean that the temporary increase in power lost during overvoltage cannot be effectively dissipated as heat. As a result, even a slight increase in the supplied power causes damage to the electronics. The diagram below shows the scale of miniaturization progress over 30 years based on resistors - the miniaturization progress for integrated circuits is several times greater, which indicates the low tolerance of modern electronics to lightning discharges.
Entire content of this article together with photos is the property of Ewimar Sp. z o.o. and is legally protected. Prohibition of copying and sharing in part or in whole,
or use in publications and public presentations.




